Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43 The odds ratio here Interpretation of the odds ratio The rare disease assumption The odds ratio vs the risk ratio Odds ratios in crosssectional and cohort studies Example, wrinkle study Interpreting ORs when the outcome is common Interpreting ORs when the outcome is common For wrinkle study Sleep and hypertension study Practice95% CI (143, 616) Steps in SPSS Use Analyze Descriptive statistics Crosstabs to produce a Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence

Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates
Odds ratio vs relative risk example
Odds ratio vs relative risk example-When RR > 1, OR > 1; This calculation a ratio of two risks is what is meant by the eponymous risk ratio (RR) statistic, also known as relative risk It allows a specific number to be given for how much more risk an individual in one category bears compared to an individual in another category In the example, an individual taking the medication bears 059 times as much risk as an adult from the



1
Title Slide 1 Author Chayanit Phetcharat Last modified by Vorasith Sornsrivichai Created Date 7/3/11 AM Document presentation formatThe odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol Relative risk assessment statistics are particularly suitedOdds ratio and relative risk
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio Finally, the odds ratio avoids ambiguity by being invariant to ltheThe smaller the risk of the disease is in both groups, the closer the OR is to the RR ;Relative risk vs Odds ratio Similarities They will always agree on the direction of comparison In our example above, both will agree that wine consumers have less heart disease than nonconsumers;
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,Mainly to distinguish it from relative risk, which is the risk for one group compared to the risk for some other group Basic statistic workshop organised by The Global Health Network Nigerian Regional Faculty 13 The risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make theseOdds Ratio versus Relative Risk Odds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study − The exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort study 33 When Is Odds Ratio a Good Estimate of Relative Risk?



1




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
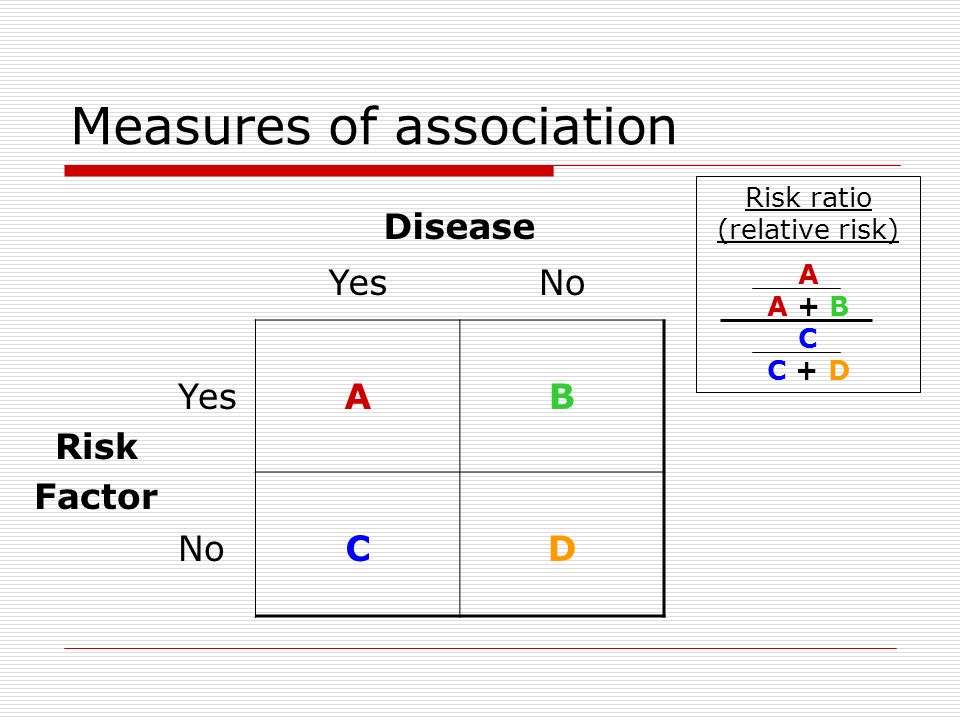
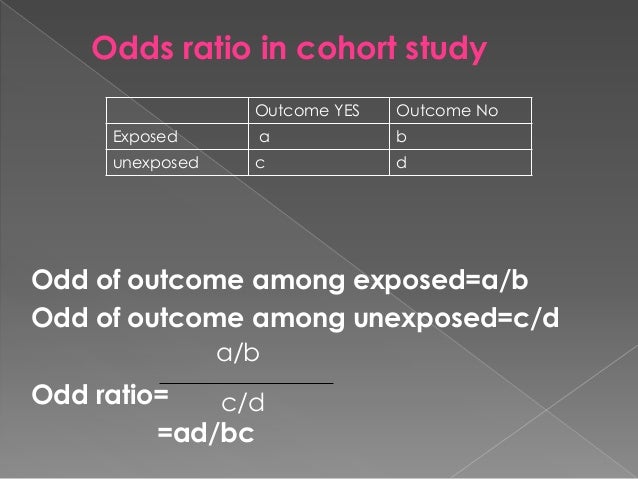
Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed) The riskRelative Risk and Odds Ratio The relative risk (RR) is the probability that a member of an exposed group will develop a disease relative to the probability that a member of an unexposed group will develop that same disease RR = P(diseasejexposed) P(diseasejunexposed) If an event takes place with probability p, the odds in favor of the event are p 1 p to1 p = 1 2 implies 1 odds;Keywords st0162, risk ratio, odds ratio 1 Introduction The case–control study design is typically (but not always) used when outcomes are rare in the population from which study subjects are sampled In 1951, Cornfield noted that when outcomes are sufficiently rare, the odds ratio from a case–control study will approximate the population risk ratio for the association of an exposure




Odds Ratio Forecasts Increase Precautionary Action For Extreme Weather Events In Weather Climate And Society Volume 4 Issue 4 12




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases
ODDS RATIO An odds ratio is the odds of the event in one group , for example, those exposed to a drug, divided by the odds of the event in another group not exposed Odd ratio in epidemiology In case control study since the incidence is not available so relative risk can not be calculated directly Therefore Odd ratio is obtained which is a measure of strength of association• risk and relative risk or • odds and odds ratio Risks and odds Risks and odds Risks A proportion Numerator / Denominator Odds A ratio Numerator / (Denominator Numerator) 2 Two by two table Outcome event Total Yes No Experimental group a b a b Control group c d c d Total a c b d a b c d Risk Risk is a proportion Risk of event in expt group = a = EER ab RiskRelative risk, the odds ratio is said to be significant if the confidence interval does not include 1 In this example the upper and lower limit of the 95% CI are both greater than 1 so the odds of death are said to be significantly higher in the control group and the result is reported as OR 3;




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Ppt Odds And Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Case Study Relative Risk and Odds Ratio John Snow's Cholera Investigations Population Information 2 Water Providers Southwark & Vauxhall (S&V) and Lambeth (L) S&V Population # Cholera Deaths 3706 L Poulation # Choleta Deaths 411 Sampling Distribution of RR & OR Goal Obtain Empirical Sampling Distributions of sample RR and OR and observeRisk ratio is similar So, for now, just get answer from SAS 95% confidence interval 086 to 304 Pvalue>05 2 Difference in proportions 2 Difference in proportionsWhat is the pvalue?




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Simple Rules On When And How To Use Them Mckenzie European Journal Of Clinical Investigation Wiley Online Library




What Is Odds Ratio Example
The odds ratio of having a DVT is 1002 and the odds ratio of not having a DVT is 1 divided by 02 or Therefore, odds ratio is often used in statistics because you can manipulate it mathematically much more easily The other common instance where odds ratio is used is for case control studies where the relative risk cannot be calculated The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups Simply divide the cumulative incidence in exposed group by the cumulative incidence in the unexposed group where CI e is the cumulative incidence in the 'exposed' group and CI u is the cumulative incidence in the 'unexposed' group The table below shows how the risk ratio wasIn our experience, equating odds ratios with relative risk has become too common, and results, even when probabilities of e vents are not small, are always interpreted as relativ e risks (Deeks



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Renin Angiotensin System Blockade After Acute Kidney Injury Aki And Risk Of Recurrent Aki American Society Of Nephrology
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02) In fact, the discrepancy between the odds ratio and the true relative risk will never be greater than the initial risk (see appendix for proof)Relative Measure of Association ("Relative Risk") o Incidence Proportion Ratio (Risk Ratio) o Incidence Rate Ratio (Rate Ratio) o Prevalence Ratio o Odds Ratio 33 Measures of Potential Impact Attributable Fraction in the Population Attributable Fraction in Exposed Cases Preventable Fraction 34 Rate Adjustment Direct adjustment Indirect adjustment (and the SMR) 1 Measures



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Quantification And Interpretation Of Attributable Mortality In Core Clinical Infectious Disease Journals The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Relative Risk Calculations Odds Ratio in CaseControl Studies (cont) Definition The amount of disease that can be attributed to a certain exposure OR, expressed as a proportion From previous relative risk example First calculate AR for group from Formulas 111 & 112 (previous slide), then use Formula 113 For proportion of the incidence in the total population, use Formula 114– Risk of the outcome in the exposed group was increased by 230% relative to the unexposed group or the outcome was 33 times more likely to occur in the exposed group than in the unexposed groupOdds ratio vs relative risk ppt INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated A crude odds ratio can



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates
Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR One of the main differences between risk ratio and hazard ratio is that risk ratio does not care about the timing The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/(ab))/(c/(cd)) = (a(cd))/(c(ab)) Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of these metrics Yet odds ratio is strongly preferred as the "right" metric to report in almost all scenarios ThatBecause in statistics odds are converted to the 'to one' standard we need to think about how we can consider the odds in favour of surviving which at present is none_death to deaths = 1 to nine = 19 = 1/9 = to convert this to the 'to one' standard we just divide each by the denominator (ie 9) so now we have the ratio of



1




Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad
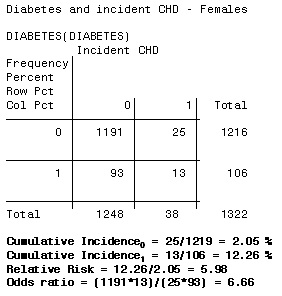
When RR = 1, OR = 1; If the disease condition (event) is rare, then the odds ratio and relative risk may be comparable, but the odds ratio will overestimate the risk if the disease is more common In such cases, the odds ratio should be avoided, and the relative risk will be a more accurate estimation of risk Absolute risk is the actual risk of some event happening given the current exposure ForThe relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used for




Effect Size Reporting Among Prominent Health Journals A Case Study Of Odds Ratios Bmj Evidence Based Medicine




Ppt Case Study Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Powerpoint Presentation Id
Understanding Relative Risk, Odds Ratio, and Related Terms As Simple as It Can Get Chittaranjan Andrade, MD ABSTRACT Risk, and related measures of effect size (for categorical outcomes) such as relative risks and odds ratios, are frequently presented in research articles Not all readers know how these statistics are derived and interpreted, nor are all readers aware of theirWhen the "cases" studied are representative of all people with the disease in the population from whichWhen RR < 1, OR < 1;




Relative Powerpoint Templates Ppt Slides Images Graphics And Themes




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download
Risk ratio (relative risk) Risk ratio calculation Inferences about risk ratio Is our observed risk ratio statistically different from 10? If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all If it's above 1, then the tutored group actually had a higher risk of failing than the controls Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the odds of an event in the control group The term 'Odds' is commonplace, but notInterpreting Odds Ratios An important property of odds ratios is that they are constant It does not matter what values the other independent variables take on For instance, say you estimate the following logistic regression model 1685 x 1 0039 x 2 The effect of the odds of a 1unit increase in x 1 is exp(1685) = 118




Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad




The Epidemiology Of Estrogen Replacement Therapy And Alzheimer S Disease Neurology
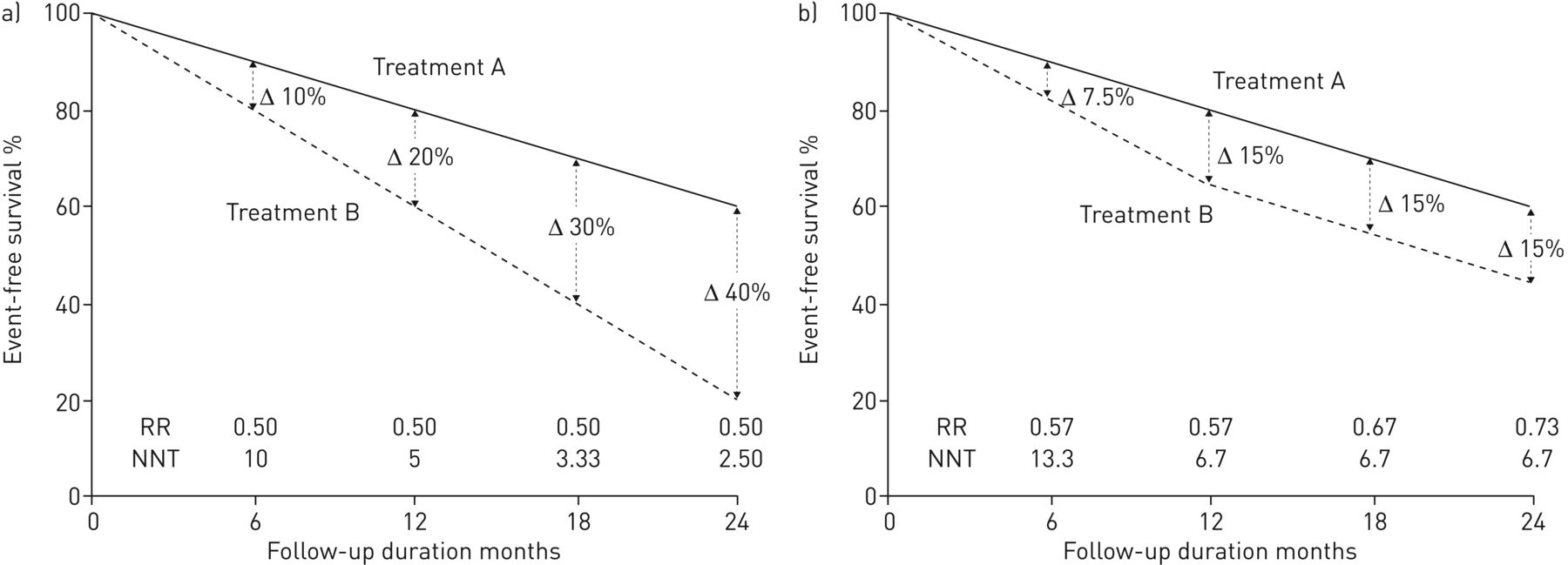
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group However, this wouldOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk Janez Stare1 Delphine MaucortBoulch2 Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that would be true But since such perception is mostly correct, there is nothing (or almost nothing) wrongSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download
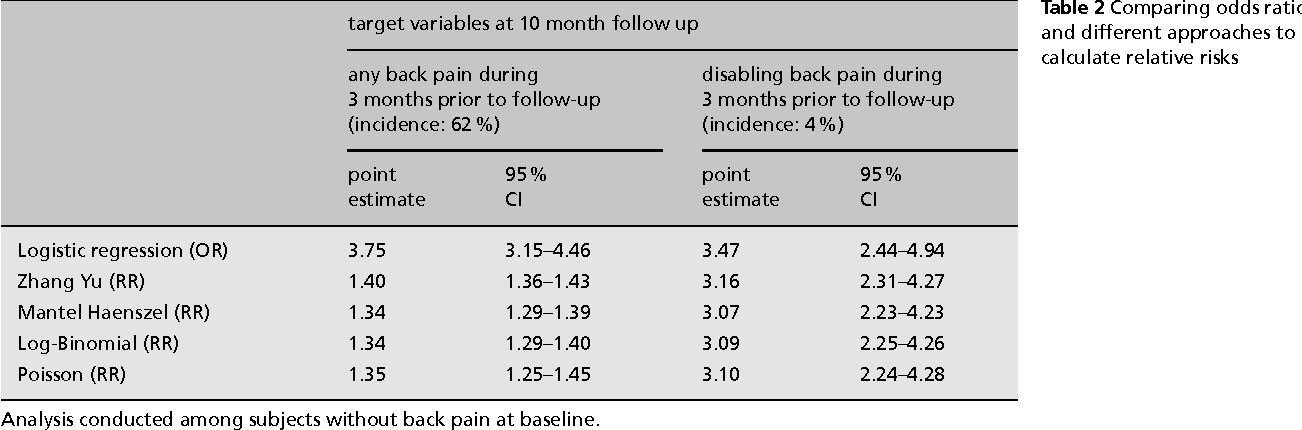
I'm going to present statistical inference for odds ratio; – Risk of the outcome in the exposed group was reduced by % (or occurred % less) relative to the unexposed group 2 What is the interpretation of a RR of 330?Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, and in cohort studies in which the outcome occurs in less than 10% of the unexposed population, the OR provides a reasonable approximation of the RR However, when an outcome is common (iY 10% in the unexposed group), the OR will exaggerate the RR One



Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease From Antiretroviral Therapy For Hiv A Systematic Review




Racial And Ethnic Differences In Treatment And Outcomes Of Severe Aortic Stenosis A Review Jacc Cardiovascular Interventions
The ratio of the risk of healing in the elastic bandage group to the risk in the inelastic bandage group is called the risk ratio For Table 4, the risk ratio = 0538/0284 = 1 The risk ratio is also called the relative risk and the rate ratio, all of which can be conveniently abbreviated to RRA risk ratio, rate ratio, odds ratio or prevalence ratio of 10 is obtained when, for a risk ratio for example, the risk of disease among the exposed is equal to the risk of disease among the unexposed Statistical testing focuses on the null hypothesis, which is a statement predicting that there will be no association between exposure and the health outcome (or between the assumed The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds ODDS RATIO Odds Ratio = Odds of Event A / Odds of Event B For example, we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball The probability of picking a red ball is 4/5 = 08 The odds of picking a red ball are (08) / 1(08) = 08 / 02 = 4 The odds ratio for picking a red ball compared to a green ball is




Risk Factors For Early Onset Ischemic Stroke A Case Control Study Journal Of The American Heart Association




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice
Odds Ratio and Relative Risk are examined in epidemiological context Odds ratio can mislead if a "Common Event" is studied, since it can exaggerate effects Relative Risk merupakan perbandingan antara dua peluang yang sukses Relative risk sacara umum menyatakan peluang terjadinya suatu kejadian (resiko) Sama halnya dengan odds ratio, sebelum menghitung risk relative terlebih dahulu ditentukan grup 1 dan grup 2 Nilai relative risk akan berkisar dari nol sampa tidak hingga Sama halnya dengan odds ratio jika nilai relativeDifferences Relative risk and odds ratio



Ppt Odds Ratio Powerpoint Presentation Free To View Id 3c00a6 Mzu3o




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
It is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in one group to the odds of it occurring in another group, or to a samplebased estimate of that ratio – PowerPoint PPT presentation Number of Views 710 Avg rating30/50 Slides 12




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Relative Measures Of Association For Binary Outcomes Challenges And Recommendations For The Global Health Researcher



1




完了しました Odds Vs Risk Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Case Control Study bestpict8tek




The Incidence Risk Factors And Prognosis Of Acute Kidney Injury In Adult Patients With Coronavirus Disease 19 American Society Of Nephrology




Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World




Circulating Mirnas And Risk Of Sudden Death In Patients With Coronary Heart Disease Jacc Clinical Electrophysiology




Estimating Risk




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Evidence Based Medicine American Academy Of Pediatrics




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Interpreting Risk Reduction In Clinical Trials For Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension European Respiratory Society




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Hazard




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Smoking As A Risk Factor For Lung Cancer In Women And Men A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Bmj Open



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Relative Risk Risk Ratio By George Peat




Contributions Of Vitamin D Response Elements And Hla Promoters To Multiple Sclerosis Risk Neurology




最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Relative And Atribute Risk




Meta Analysis Evaluating Outcomes Of Surgical Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion During Cardiac Surgery American Journal Of Cardiology




Ppt Odds Ratio Powerpoint Presentation Free To View Id 3c00a6 Mzu3o




The Absolute And Relative Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes After Gestational Diabetes A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of 129 Studies Diabetes Research And Clinical Practice




746 P Advancing Therapy In Uncontrolled Basal Insulin Treated Type 2 Diabetes T2d Nocturnal Hypoglycemia In The Solimix Trial Diabetes




Mortality Among Hospitalized Dengue Patients With Comorbidities In Mexico Brazil And Colombia In The American Journal Of Tropical Medicine And Hygiene Volume 105 Issue 1 21




Risk Factors For All Cause Hospital Readmission Following Exacerbation Of Copd A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis European Respiratory Society




Relative And Attributable Risks Ppt Download




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




The Relationship Of Covid 19 Severity With Cardiovascular Disease And Its Traditional Risk Factors A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




Social Determinants Of Health And Diabetes A Scientific Review Diabetes Care



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




Math Matters How Misinterpretation Of Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios May Influence Conclusions Academic Pediatrics




Math Matters How Misinterpretation Of Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios May Influence Conclusions Academic Pediatrics




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Relative Risk Wikipedia



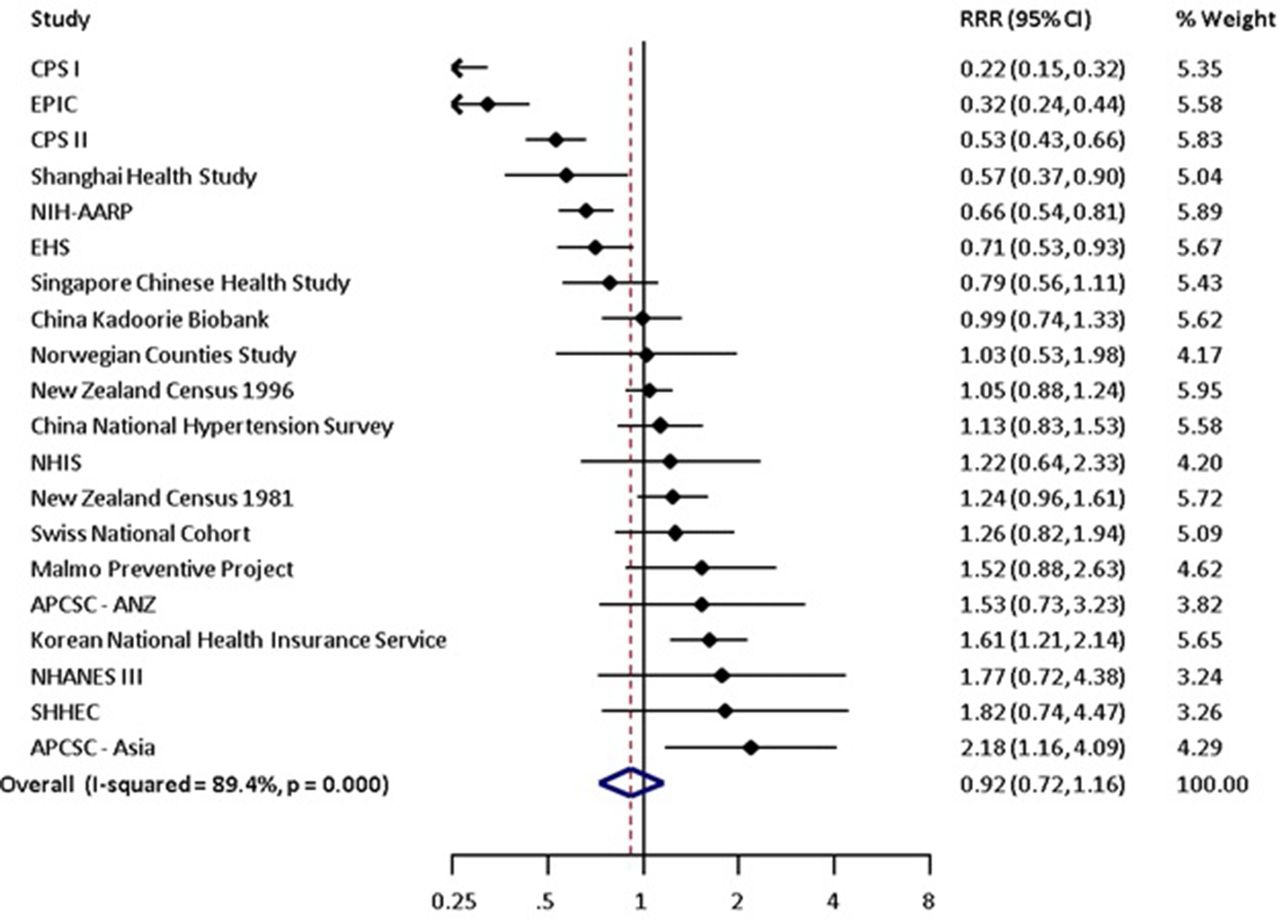
Additive Synergism Between Asbestos And Smoking In Lung Cancer Risk A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Odds Vs Relative Risk ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Dementia Prevention Intervention And Care Report Of The Lancet Commission The Lancet




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Three Main Types Of Nonexperimental Studies Crosssectional Compare




Odds Ratio Forecasts Increase Precautionary Action For Extreme Weather Events In Weather Climate And Society Volume 4 Issue 4 12



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Map To Illustrate The Odds Ratio For 5 Year Risk Adjusted Survival Download Scientific Diagram




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id



Odds Ratio




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Ppt Lesson 11 Relative Risk And The Odds Ratio Powerpoint Presentation Id



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿